IMMUNIZATION 2022 / MedUrgent
IMMUNIZATION
Definition
— Vacca: Latin = Cow
— Vaccinia: Cowpox virus
— Developed by Dr. Jenner in 1797
— Vaccination= Inoculation with the virus of vaccinia (cowpox) to protect against smallpox
Vaccine:
— A preparation of attenuated (weakened)or killed micro-organism, toxoid or genetically engineered antigenic material administered for the prevention of infectious disease
— EPI: Started in 1978
— Universal Immunization Program: Introduced in 1985
— Immunization: The act of rendering immune
— Active Immunity: Giving regular doses of vaccine
— Passive Immunity: Giving Antibodies
Cocooning Strategy of vaccination:
— Vaccinating Pregnant ladies, lactating mothers, Sibs, Fathers and Grand Parents (TdaP)
Live attenuated Vaccine:
— Weakened organism that produces antigenic response without serious infection
Killed Vaccine:
— Organism is killed or the antigen is inactivated by heat, phenol, formaldehyde or other methods
Conjugated vaccine:
— Polysaccharide vaccine (H. influenza) conjugated with DPT to stimulate T cells and thus eliciting immunological memory
Toxoid:
— Toxins rendered non-toxic (by formaldehyde) but antigenicity is maintained
Vaccine Handling & Storage
— Recommended temp.2- 8 °C
— OPV: <0°C (thawing and refreezing NOT more than 10 times)
— Varicella: <-15°C (reconstituted: use within ½ hr)
— MMR: Reconstituted: use within 8 hrs.
— Always: check the manufacturer package insert
— Revise the Cold Chain: shipment to customer
Personnel & Equipments
— One person responsible
— Working refrigerator and Electric Stabilizer
— Thermometer
— Frozen water bottles or ice packs
— Vaccines: in the central storage area
— NO food or other drugs
Vaccine administration
— ≤ 1 yr: Antero-lateral aspect of the thigh
— > 1 yr: Deltoid
• Buttocks: ↑subcutaneous fat + Sciatic nerve
• Deep i.m. (needle = 7/8 – 1 inch long)
• Same site for s.c. (Measles)
• Intra-dermal: On the volar surface of the forearm (25-27 gauge needle)
— Multiple vaccines: same (1-2 inches apart)or a different thigh
— NO mixing of vaccines in One syringe
— Gentle pressure: Relieves pain and stops bleeding
— Keep the child at his mother lap
— Local anesthetic may be used (ELMA cream or Vapo-coolant spray)
— Distracters or pacifiers
Complications
— Possible complications of i.m. vaccines:
-Nerve injury
-Infection
-Abscess
-Skin pigmentation
-Hemorrhage
-Cellulitis
-Tissue necrosis & gangrene
-Scars / cysts /local atrophy
-Periostitis
 |
Special Considerations
— For patients with Bleeding tendency: Give the i.m. vaccine immediately after giving the replacement factor
— Press for 2 min.
— Subcutaneous root is safer
— After giving IgG: Wait for 3-5 months to give live vaccines
— Wait for 2/52 after live vaccine to give IgG
— Pre-terms: Vaccination according to the chronological age
— A lapse : NO reinstitution, continue vaccination as scheduled
— No documentation: Start from zero
— Vaccine Adverse Events: Report to MOH
— Oral vaccine, spitted or vomited: Repeat
Remarks
— Injection sites: Lateral aspect of Thigh or Deltoid
— No vaccine should be given i.v.
— Fever : Analgesic
— Live vaccines: Not given to immuno-deficient children
— Pre-terms: Vaccinated at the proper chronological age
Precautions
— Convulsions within 72 hrs: No more pertussis vaccine
— Care with children brain damage and convulsions
— During epidemic: Measles vaccine can be given at age 6/12
— OPV, Yellow Fever & Cholera vaccines should not be given together
— Check the color of the square on the sticker on each vial
— Check the color of the vaccine solution:
-Colorless (MMR, PCV, Hib…)
-Turbid (DPT-aluminum conjugate, Toxoid)
Immuno-compromised patients
— Impaired host defense
— Frequent contact with medical environment
— CDC & IDSA Recommendations (Jan.2014):
(Centers for Disease Control & Infectious Diseases Society of America)
— Live vaccines: Given 4/52 before immuno-suppression
— Influenza vaccine regularly every year i.m.(NOT the inactivated nasal spray vaccine). Age 6/12 – 49 yrs.
— Household contacts: Regular vaccination
— Complement deficiency: Normal vaccination
— HIV: Normal vaccination (Not the nasal spray Influenza vac.)
— Poor uptake of vaccines during intensive chemotherapy or in patients on anti-B cell antibodies
— Give vaccines 4/52 after immuno-therapy
— No vaccines during a course of IgG therapy
Vaccine Vial Monitoring
— Normal: inner square of the sticker is lighter than the outer circle
— Color of the square matches with or darker than the circle: discard
— Always: Check the Expiry Date
— Always : check the color of the solution
— Always: Read the Insert
NOT Contra-indications
— Mild URTI or Diarrhea
— Fever <38.5 C
— Allergy / Asthma
— Prematurity
— Malnutrition
— Breast feeding
— Family history of convulsions
— Antibiotics
— Chronic diseases e.g. CHD
— Cerebral palsy, Down’s Syndrome
Refrigerators
• Properly working
• Electric Stabilizer
• NO food, drinks or other drugs
• OPV: Freezer
• Other vaccines: Middle and lower compartments
• Thermometer
• Ice packs or frozen water bottles
• OPV : Freezer (Presence of sorbitol: does not freeze)
• Measles: Dried powder, under the freezer
• Thermometer
BCG
• Bacilli Calmette & Guerin
• Attenuated bovine mycobacterium
• Wheal: for 1/2 hr
• Nodule: After 3/52
• Ulceration & healing with a scar: 4-6/52
• Koch’s phenomenon: Accelerated reaction (10days)
• Complications: Erythema nodosum, abscess, ulceration, local lymphadenopathy and generalized T.B
• B.C.Giosis: Generalized T.B. secondary to vaccination
• No scar after 4/12:
- Repeat vaccine
-Still no scar: repeat after ONE yr
• Intra-dermal
• At birth: (0.05ml)
• Older children: (0.1ml), Mantoux test first
• Efficacy: 0 – 86%
• Bacille Calmette & Guerin
• Live attenuated mycobacterium bovis
• Elder children: Mantoux test first
• Immunity wanes after 10-15 yrs
• Nodule (2-3/52), Ulcer (4-6/52), healing with a scar (2-3/12)
• Complications: erythema nodosum, deep ulceration, abscess, lymphadenopathy, generalized disease
OPV (Oral Polio) – Sabin
• Live attenuated type I, II, III
• Efficacy: 90 - 98%
• Protection is life long (within 1/52)
• Superior to IPV in antibody response
• Provides herd immunity
• Not given to HIV, Immuno-compromized and immunosuppressant drugs users)
• Rarely: causes paralytic polio
• IPV: Less potent but no paralytic polio
Inactivated Polio vaccine(IPV)-Salk
— Given i.m./ s.c.
— Less immunogenic
— Does not cover the GIT
— No herd immunity
— No spread to pregnant ladies
—
Pentavalent
• DPT + HiB + HepB
Diphtheria
— Anti-diphtheritic human Immunoglobulin:
*Prophylactic = 300 IU -i.m.
*Therapeutic =1200 – 20000 IU –i.m.
— Antidiphtheritic Serum:
*Used when IgG is N.A.
*Horse serum: Test for allergy
*Prophylactic = 10000 IU –i.m.
*Therapeutic = 40000 – 120000 IU –i.m.
— Formaldehyde inactivated toxin & adsorbed onto aluminum salt to increase antigenicity
— Does not protect against the bacteria itself
— Efficacy: >87%
— Dose: 0.5 ml – i.m.
— TD (for children when P is contraindicated) contains 10-20 Lf, causes severe reactions in adults
— Td (1-2 Lf) used for adults.
Pertussis
— Whole cell vaccine or part of cell wall (aP)
— Efficacy: ≈80%. Immunity wanes with time
— Dose: 0.5ml – i.m.
— Contraindications:
*Encephalopathy within 1/52 of a previous dose
*Anaphylactic reaction to the vaccine
— Side effects:
*Fever > 40° C
*Collapse / Shock
*Seizures
* Inconsolable crying
* G-B Syndrome
*Acute encephalopathy
*Permanent neurological sequelae
Haemophilius Influenza type B
— Conjugated and combined with other vaccines
— Effective and very safe
— Dose: 0.5ml – i.m.
— Adults: one dose only
—
Tetanus Immunoglobulin (TIG)
• Prophylactic (250 IU – i.m.)
• Therapeutic (1000 – 10000 IU – i.m.)
• Protects for 30 days
Tetanus Toxoid (TT)
• Formaldehyde- inactivated tetanus toxin
• Stable (up to 37° C)
• Efficacy: >95%
• Given even after clinical disease
• Very rarely: Anaphylaxis, G-B Syndrome & brachial neuritis
Tetanus Antitoxin (ATS)
• Protection for 7 -15 days
• Horse serum (do sensitivity test)
• Prophylactic :
1500 – 3000 IU – i.m.)
• Therapeutic:
40000 -60000 IU (half i.m. +half i.v.)
• Neonates:
-10000 IU – s.c. around umbilicus
-10000 IU – i.m.
-10000 IU – i.v.
Rota vaccine
• Rotarix: Monovalnt (RV1) attenuated
• Rotarig: Pentavalent (RV5) v produced by reassorment)
• Oral:1.5 ml
• Given: 1st. Dose NOT later than age 100 days.
• 2nd. Dose NOT later than 8/12
• A 3RD. Dose of ROTARIG may be given at age 6/12 (NOT Rotarix)
• VAE: Intussusceptions (1/100000), allergy, Diarrhea& Vomiting
• Contamination with Circovirus particles: Not harmlful
Pneumococcal
• Capsular antigen
• Available: 7,10,13,23 serotypes (>80 serotypes of pneumococci)
• Limited activity at age <2 yrs.
Pneumococcal Vaccine: PCV 23
— Pneumococcal polysaccharide
— Polyvalent :23 serotypes
— Age: >2 yrs
— 3 doses
Pneumococcal Vaccine: Synflorix
— Polysaccharide 10 valent
— Contains small amounts of Hib, Tetanus toxoid and Diphtheria carrier proteins
— Age: <2 yrs
— Dose: 0.5 ml – i.m.
— 3 doses
Pneumococcal Vaccine: Prevenar 13
— Contains 13 serotypes
— Doses:
-Age 7 – 11 months: 3 doses one month apart
-Age 12 -24 months: 2 doses two months apart
-Age > 2yrs – 5 yrs: One dose
-Age > 50 yrs: One dose
Pneumococcal
• Dose 0.5ml i.m or s.c.
• Recommended for high risk patients: HSS, splenectomy, CRF, immuno-suppressed, HIV, CSF leak
Hepatitis B
• Inactive unit of the virus (not infectious)
• Efficacy: 80 -95%
• Given to infants born to HBsAg +ve mothers with HBIG (different sites)
• Exposed children: Check anti-HBs (level of antibodies to HBsAg),
* -ve: revaccinate
*+ve: ( >10 mIU/ml), no need
Hepatitis A
• Attenuated
• Mostly during epidemics or for contacts, liver transplant and
–ve. adolescents
• Dose: 0.5ml -720 (1 ml for adults - 1440)
• Children > 1 yr: two doses, 6/12 apart
• ??One booster after age 5yrs
Measles vac
• Live attenuated
• Efficacy: 85 -90%
• 0.5ml s.c.
• May cause fever, rash, convulsions and encephalitis
• Can be given 72 hr. post-exposure to measles
• Can not be given to patients with allergy to neomycin, immuno-deficients and pregnant ladies,
MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella)
• Live attenuated in lyopholized powder + diluent
• S.c./i.m.
• 1st.dose: 1 yr - 15/12
• 2nd.dose: 4 – 5 yrs
• Not given during pregnancy (Rubella)
• No pregnancy 2/12 after vaccination
• Leads to –ve Mantoux test:
-Do the Mantoux test before the vaccine
-OR: do them simultaneously
-OR do Mantoux test 6/52 after MMR
Combination Vaccines
Why?
-High immunogenicity
-Less pricks
-Less visits
-Less cost
-Increased compliance
Examples:
-DPT, Td, Pentavalent
-Infanrix hexa (Pentavalent + IPV)
-Priorix tetra (MMR + Varicella)
Immunization Schedule
— Varies: Why?
-Disease risk
-Age-specific immune response
-Vaccine availability
-Maternal vaccination
— High level of protection: Single dose vaccines e.g. Rubella
— Mostly give 85-98% coverage
Vaccination Schedule
EPI – Sudan
|
Age |
Vaccine |
Dose |
Route |
|
Birth |
BCG+OPV |
0.05ml – 2drops |
Intradermal - Oral |
|
6/52 |
Pentavalent + OPV+ PCV+
Rota + IPV |
0.5ml+2drops + +1.5ml |
i.m + Oral + Oral +im |
|
10/52 |
Pentavalent + OPV +PCV+PCV |
0.5ml+2drops |
i.m + Oral |
|
14/52 |
Pentavalent +OPV + PCV +Rota + IPV |
0.5ml+2drops + 1.5ml |
i.m + Oral + Oral |
|
9/12 |
Measles +Meningitis + Yellow Fever |
0.5ml |
Subcutaneous + im+ im |
Tetanus Vaccine for pregnant ladies
Late Arrivals (≥ 7yrs.old)
Meningococcal
— Commonest serotypes of meningococci are A (epidemics), B (endemic, poor antigenicity), C, W-135 & Y.
— Short duration immunity (not for routine immunization)
— Important for children with splenectomy or hypo-complementaemia
— A: for age >3/12 (During epidemics -2doses )
— C: for age >2 yrs
— Not given before age 2yrs
— Efficacy: Wanes with time. Repeat every 5 yrs
— Dose: 0.5ml – s.c.
— Does not protect against B
Meningococcal Quadrivalent vaccine (A,C,W-135 & Y)
(Peter M Dull–( Reuter, Health Information) – Jan. 2014
— Multinational study
— In USA, Infants <7/12 are more vulnerable to meningococcal infections than 14 – 24 yrs old
— Results support the expanded indication for infants as young as 2/12 of age
— Vaccine is well tolerated and highly immunogenic when given with the routine childhood vaccines
— Rate of Serious Adverse Events remained the same
Varicella
— Lyophilized powder of live attenuated virus (Oka stain)
— Age >1 yr
— Dose: 0.5ml – s.c. ( For adolescents:2 doses one month apart)
— Efficacy: 90 – 97%
— NO use of Salicylates for 6/52 following vaccination (Reye’s Syndrome)
— Contra-indicted during pregnancy
— Mild rash after vaccination
— For immuno-compromized patients:
-No vaccine for patients on Radiotherapy
-Stop chemotherapy One week before and One week after vaccination
-Others (HIV, malignancy, auto-immune diseases, CRF, collagen diseases, after transplant, steroid therapy..), Lymphocyte count should be above 1200/mm³
-Very rarely: causes Herpes zoster and cerebellar ataxia
Typhoid
— Vi- antigen
— Dose: 0.5ml – i.m.
— Efficacy:<66%
— Start at age 2 yrs, then every 2 yrs
Cholera
— Efficacy of the injectable vaccine: Only 50%
— Dose: 0.2ml -0.5 ml – i.m.
— Boosters every 6/12
— Oral vaccine are more powerful:
1-Whole-cell-B subunit (also protects against Entero-toxigenic E.coli)
2-Live attenuated vibrio
Rabies
— Human Diploid Cell Vaccine (HDCV):
*Pre-exposure:
-Dose: 1 ml –s.c. or i.m.
-2 doses, one month apart, then a 3rd. Dose after 1 yr., then after 3- 4 yrs
*Post-exposure:
-Dose: 1 ml at days 0, 3, 7, 14 & 28
— Passive Immunization:
1- Human Rabies Immunoglobulin
*Dose: 20 IU/kg – half i.m. and half around the wound
2- Rabies Anti-serum
*Dose: 40 IU/kg – half i.m. and half around the wound
Vaccine Adverse Events
— Anaphylaxis (serum)
— Paralytic polio (OPV)
— Encephalomyelitis (Measles)
— Seizure (Pertussis)
— Inconsolable crying (DPT)
— Hypotension (DPT)
— Local reactions (Aluminum conjugate)
— Lymphadenitis (BCG)
Proposed Comprehensive Schedule
Other available vaccines
— Adenovirus
— Anthrax
— Influenza
— Japanese Encephalitis
— Lyme disease
— Pigbel (against Clostridium perfringens)
— Plague
— HPV (Human Papilloma Virus causes cervical, penile and anal cancer ).
- Given at age 9-18yrs for both sexes
- Simultaneously with other childhood vaccines (TdaP, OPV, meningitis…..)
— Covid 19 : will be addressed separately
Vaccines under development
— Dengue
— E.coli
— Hepatitis C
— HIV
— Malaria
— Meningococcal B
— Para-influenza virus
— Respiratory Syncitial Virus
— Shigella
— Schistosomiasis
— Dengue
— E.coli
— Hepatitis C
— HIV
— Malaria
— Meningococcal B
— Para-influenza virus
— Respiratory Syncitial Virus
— Shigella
— Schistosomiasis


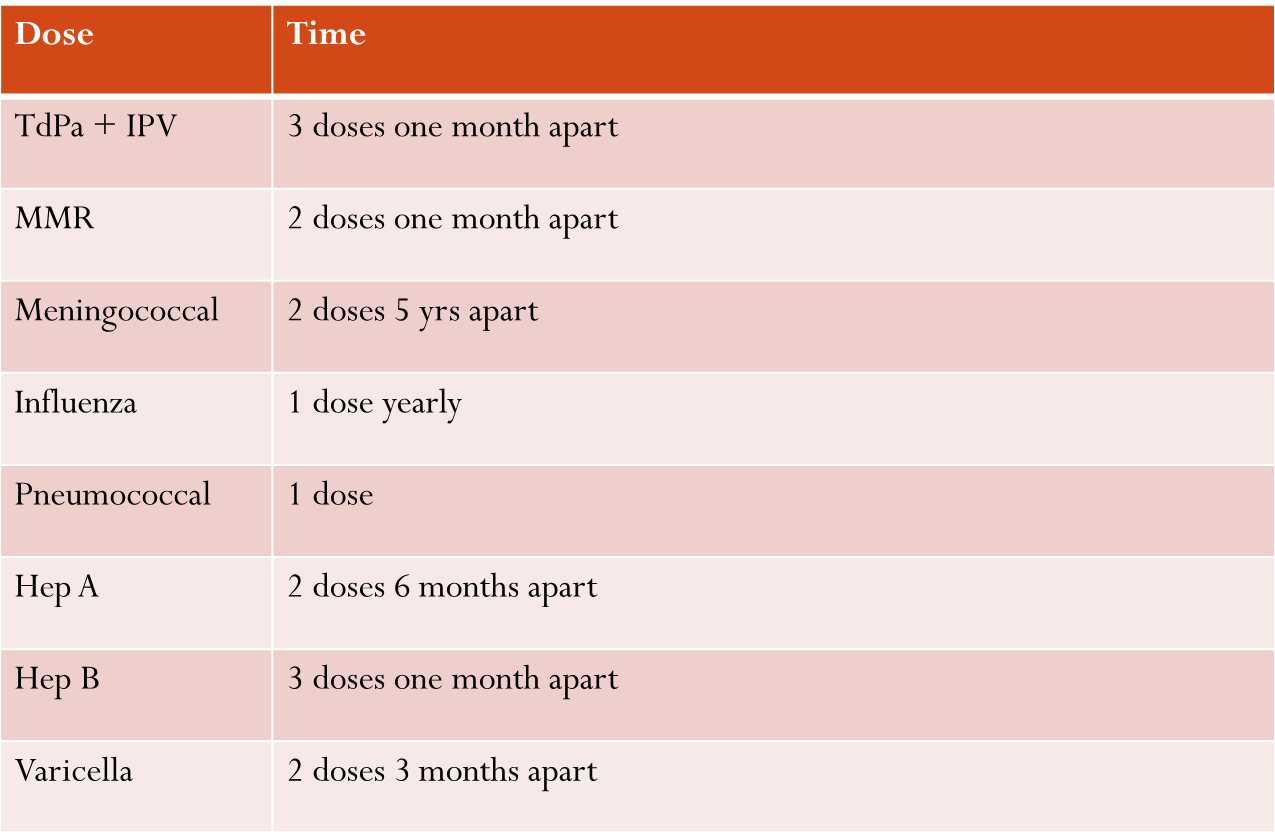




Comments
Post a Comment